Several years ago, businesses began to realize that data was soon becoming the new currency. Fast forward to today, and the conversation has shifted to AI. But here’s the catch: many organizations still don’t have a proper grasp of their data environments.
Sure, AI is being used in isolated projects, but to truly unlock its potential to drive accurate business predictions, streamline operations, and enable automation, data needs to be gathered, organized, and made accessible to business users in a clear, understandable way.
That’s what this blog is here to unpack. We’ll help you understand your data environment better and explore how Fortude’s Lakehouse Accelerator can help you build a scalable data structure that grows with your business. You’ll also see real-world use cases of how this accelerator is helping global businesses set up data architectures tailored to their unique needs.
Mapping your data environment with our accelerator
The easiest way to understand your data architecture is to view it like you would your own home. A home without a foundation would not stand, and it is the structured elements or layers of a home that give it a cohesive look.
So, let’s take a look at each of these layers and the roles they play in your data architecture, and in parallel look at how our Lakehouse Accelerator steps in at each of these junctures to give structure and drive efficiency across the layers.
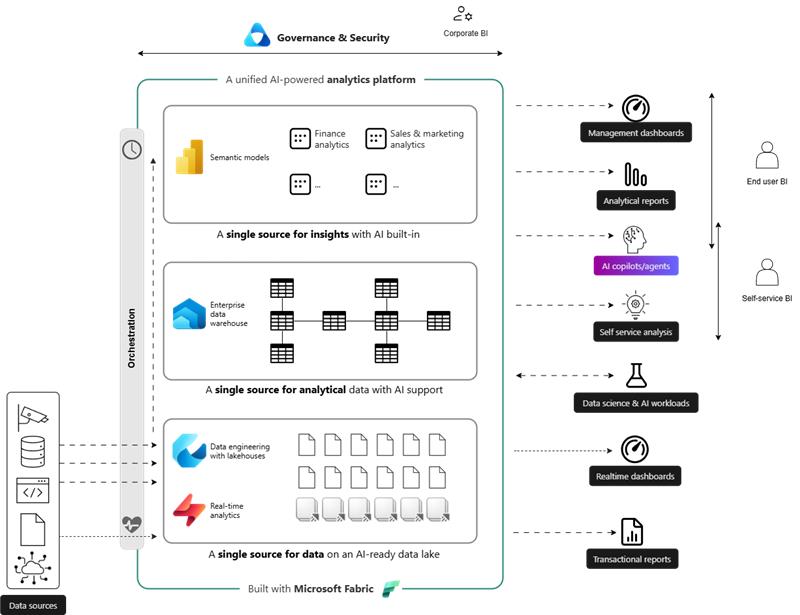
- Layer 1: The lakehouse (single source of data) – If you’re wondering what a lakehouse is, it’s essentially a place that stores all kinds of raw data, structured or unstructured, in one central location. Whether it’s from your enterprise resource planning (ERP) system, customer relationship management (CRM) system, warehouse management systems, or even media, this foundational layer brings all that data together to live in one place.
The role of our accelerator: The Lakehouse accelerator plays an important role at this stage because it fast-tracks the implementation of this foundational layer. The accelerator has pre-built pipelines that bring all this data together to the lakehouse, and more importantly, it can be customized accordingly to suit your own unique requirements and data sources.
- Layer 2: The data warehouse (single source of analytics) – This is where the data from the lakehouse is transformed and merged into analytical data. On top of this data, standard organization-wide business logic is applied. It can be used to model the data so it can be used for different use cases. This allows your teams to analyze metrics across functions, identify trends, and make decisions based on a complete view of the business, rather than piecing together data from multiple places. For example, sales data from your CRM, inventory data from your ERP, and marketing data from your campaigns can all be combined in the warehouse to target products to specific customer segments.
The role of our accelerator: Despite it being called the lakehouse accelerator, our solution also sets up the structure for this layer as well so you have the freedom to customize it quickly based on business needs.
- Layer 3: Semantic models (self-service analytics) – This additional layer allows you to apply a set of function-specific calculations and business logic making it intuitive for non-technical end users to easily understand their data. For instance, the marketing team will be able to drag and drop the metrics of a campaign into a canvas and easily build a report to quickly understand the granularities of performance.
The role of our accelerator: To this layer too, the lakehouse accelerator provides structure on top of which Fortude consultants can come in, talk to you , and build the metrics to suit your requements. In addition, we have pre-built analytics accelerators such as the sales and finance ones to help you easily set up and get started. We will talk about these accelerators in detail in the next blog in this series.
Fortude’s global success: One accelerator, many possibilities
- An international footwear company based in New York designs, sources, and markets footwear for men, women, and children through its own brands. The company also offers private-label products for major retailers and distributes through both wholesale and direct e-commerce channels.Their data journey ran through multiple systems like their ERP and disparate files on SharePoint, making it difficult to access a unified view of information. To overcome this, the company adopted Fortude’s Lakehouse Accelerator which fast-tracked implementing all three layers: the lakehouse, data warehouse, and semantic model for sales, marketing, and procurement. This approach gave them a structured, scalable architecture that made their data easily accessible and actionable across the organization.
- A US-based, family-owned supplier of school uniforms, medical attire, and gym wear. The company implemented the Lakehouse Accelerator for the foundational layer to bring together data from disparate sources including their ERP. On top of this platform, their in-house technical team are exploring multiple options including building their own data marts and semantic models.
- An Australian diversified business group was preparing to modernize its core operations by implementing a new ERP, replacing its legacy ERP system. As the new ERP was handling ongoing transactions and the legacy system was retaining historical data, the group needed a unified architecture to connect both systems and create a single source of truth.The company used Fortude’s Lakehouse Accelerator to build a unified data platform that integrates ERP and Excel data for enterprise reporting. Fortude also delivered an enterprise data warehouse, data models and dashboards across Sales and Finance, combining 50+ key metrics into a unified analytics model.
- A global fashion brand headquartered in New York, known for its trend-driven footwear and accessories, took its first step toward building a unified data foundation with Fortude’s Lakehouse Accelerator. The accelerator was set up as the starting point, with the technology now in place to pull and push data in near real time, enabling the brand to access operational insights and make faster, data-driven decisions.
Next steps?
So, if your organization is looking to understand how your data architecture can support your growth ambitions and prepare for better AI integration, don’t delay. Start with a data assessment to understand where you stand today, how your current architecture aligns with your data strategy, and how you can build a scalable foundation for the future.
Interested in learning more about Fortude’s Lakehouse Accelerator? Get in touch with our data experts and stay tuned for the next blog in this series, where we’ll explore Fortude’s Sales and Finance Accelerators in detail.
Talk to our data experts today.
FAQs
A data architecture is made up of three layers: the lakehouse (single source of data), which brings together all raw data; the data warehouse (single source of analytics), where data is transformed for analysis; and semantic models (self-service analytics), which apply business logic to make data easy for non-technical users to explore and understand.
Fortude’s Lakehouse Accelerator fast-tracks the setup of a lakehouse-oriented data architecture. It uses pre-built pipelines to bring together data from multiple systems, helping organizations establish a strong foundation for analytics. The accelerator also supports building data warehouses and semantic models, allowing businesses to move from fragmented data to a unified, scalable analytics environment.
Yes, the Lakehouse Accelerator is flexible and can be tailored to an organization’s unique data sources, systems, and reporting needs. Fortude’s consultants work with teams to configure data pipelines, models, and metrics, ensuring the platform aligns with business goals and provides the agility to evolve as data requirements grow.
A well-structured data architecture lays the foundation for successful AI adoption. By bringing together clean, organized, and accessible data through layers like the lakehouse, data warehouse, and semantic models, organizations can ensure their AI models are trained on accurate information, enabling smarter predictions, process automation, and data-driven decision-making across the business.
Subscribe to our blog to know all the things we do